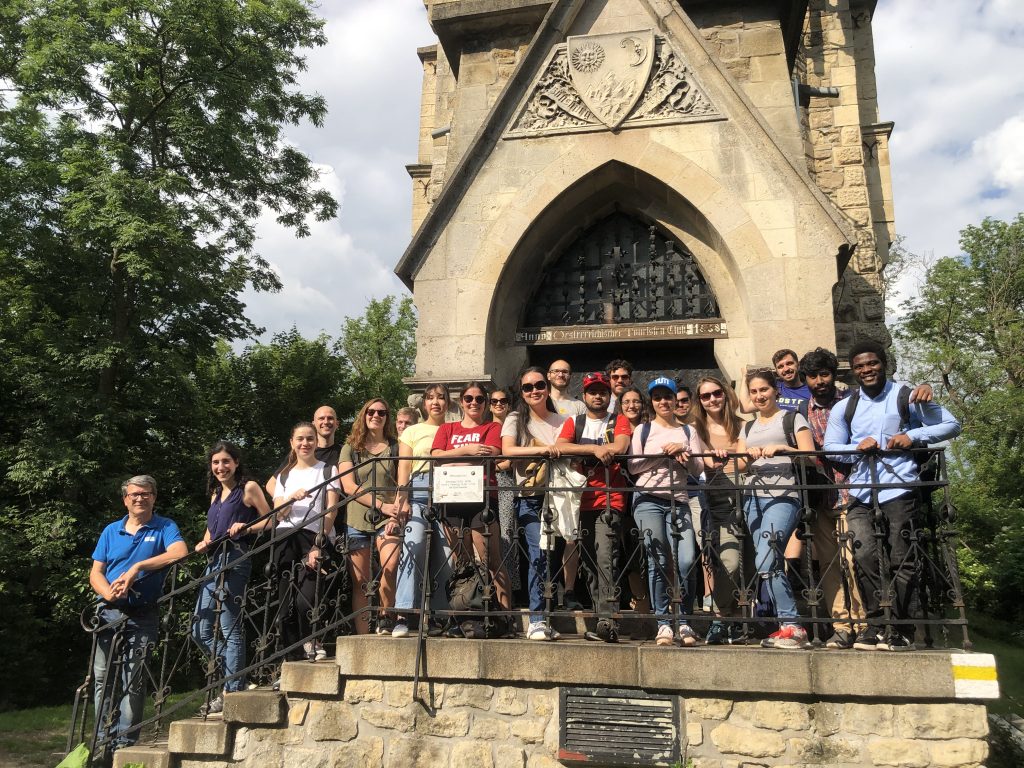
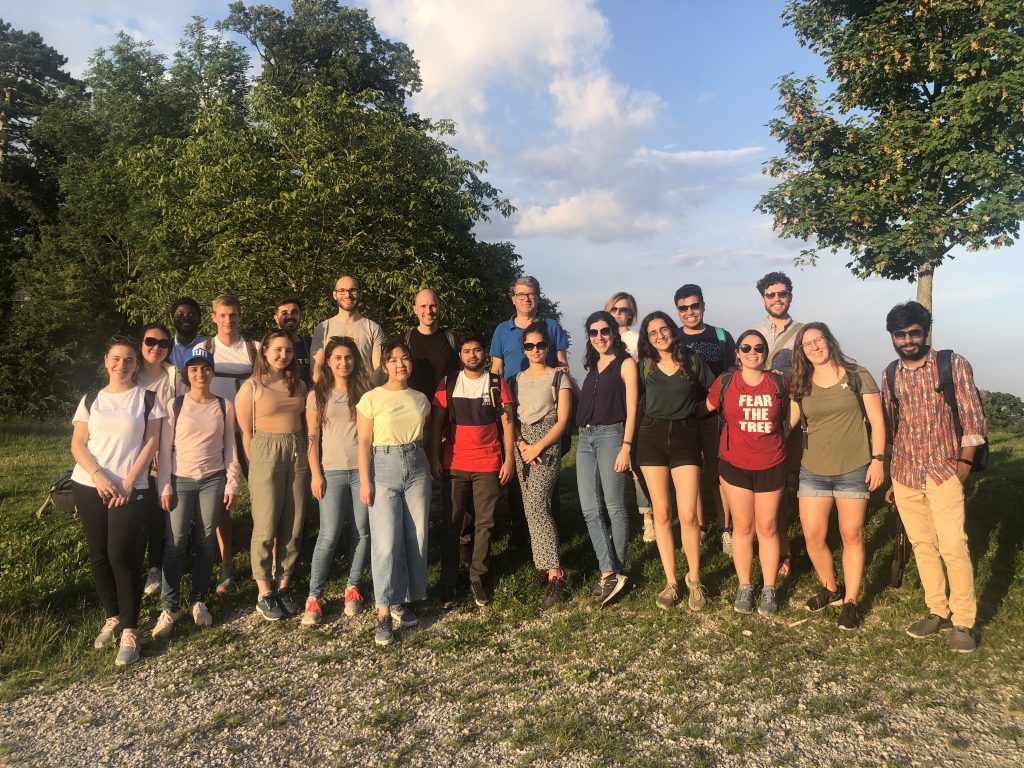
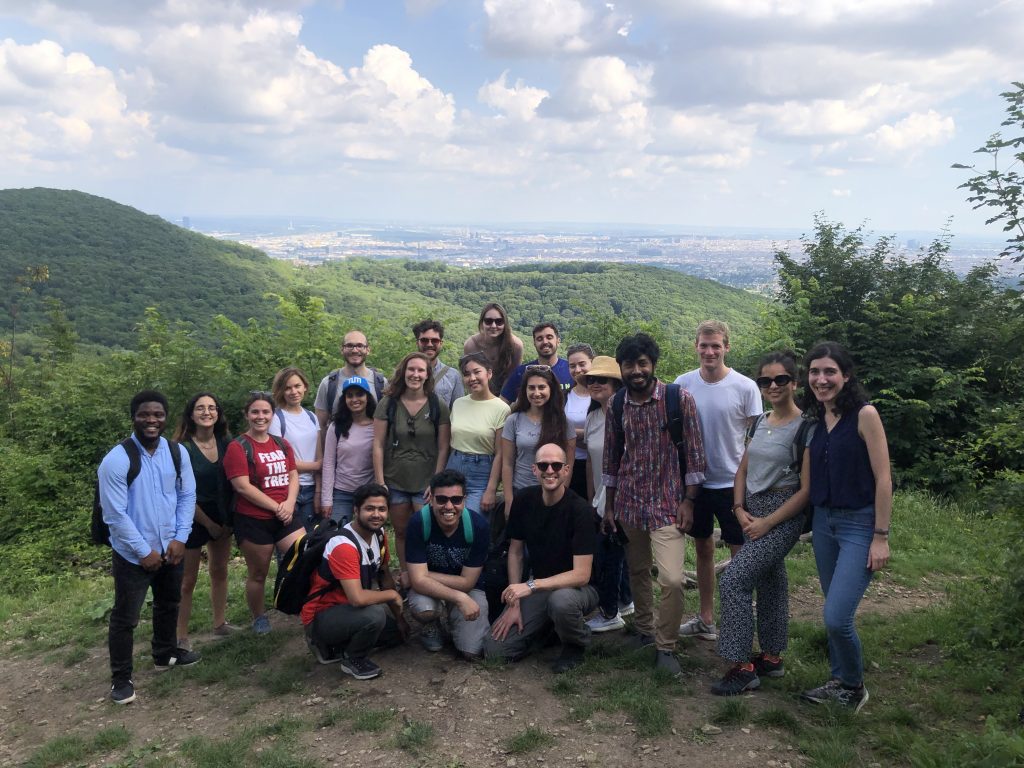
Together with our students of the International Master of Cartography, we went on a hike to Hermannskogel last week. In perfect weather conditions, we reached the highest natural point of Vienna – at 542 metres above sea level. Atop the Hermannskogel, we visited the Habsburgwarte, which marked the kilometre zero in cartographic measurements in Austria-Hungary until 1918.
Affective Communication of Map Symbols ‒ Paper by Silvia Klettner published in the ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information
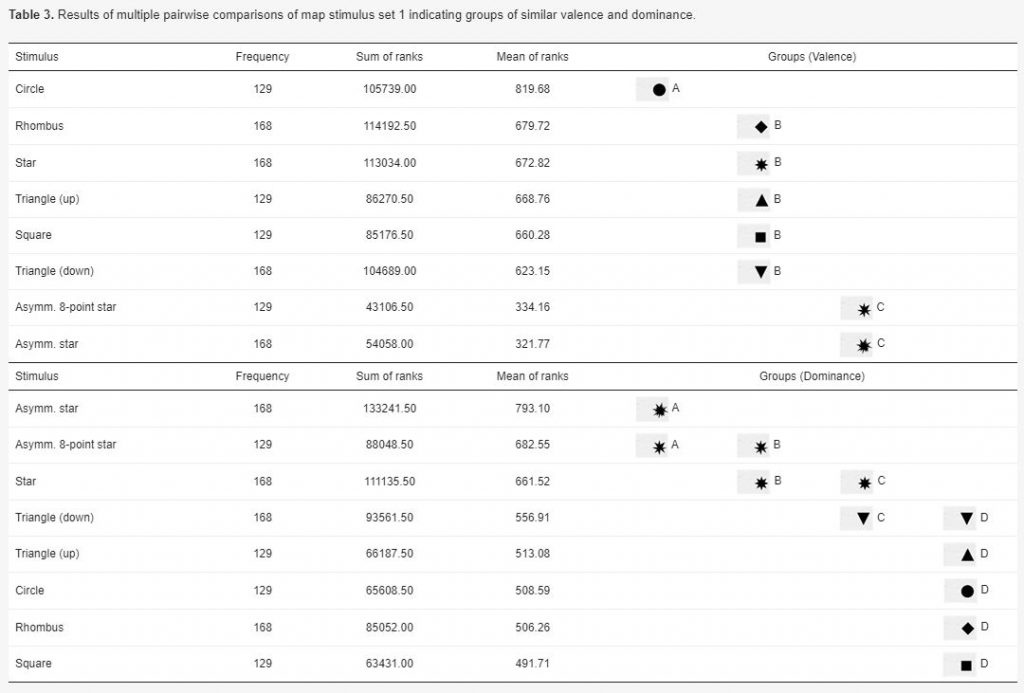
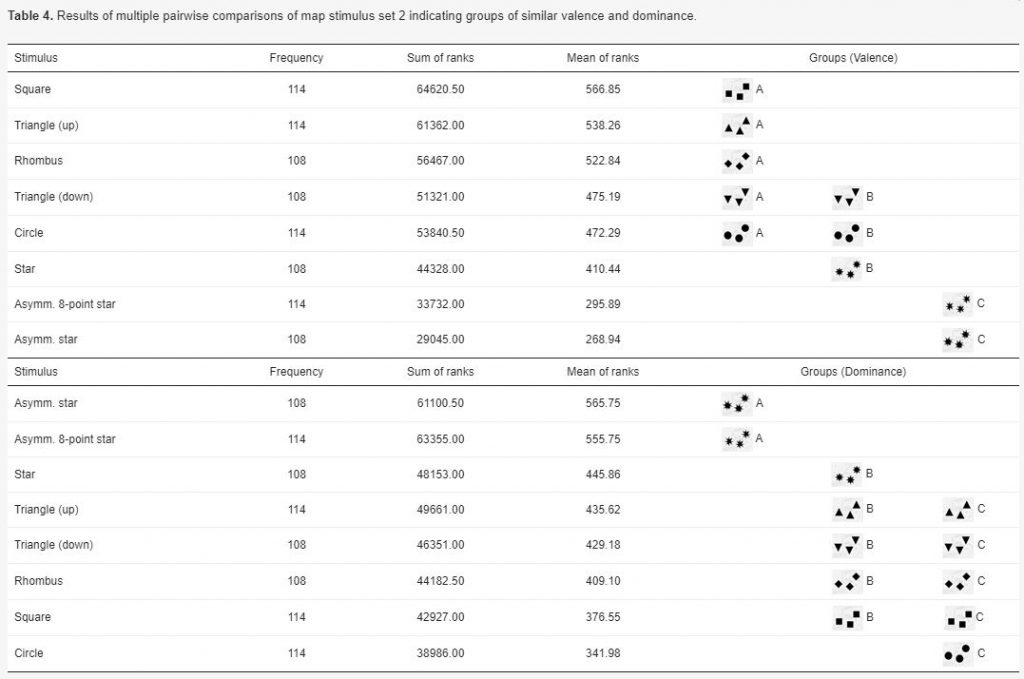
Silvia Klettner’s work on the subtle communication effects of map symbols was recently published in the ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information in the Special Issue on Geovisualization and Map Design: Klettner, S. (2020). Affective Communication of Map Symbols: A Semantic Differential Analysis. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 9(5), 289.
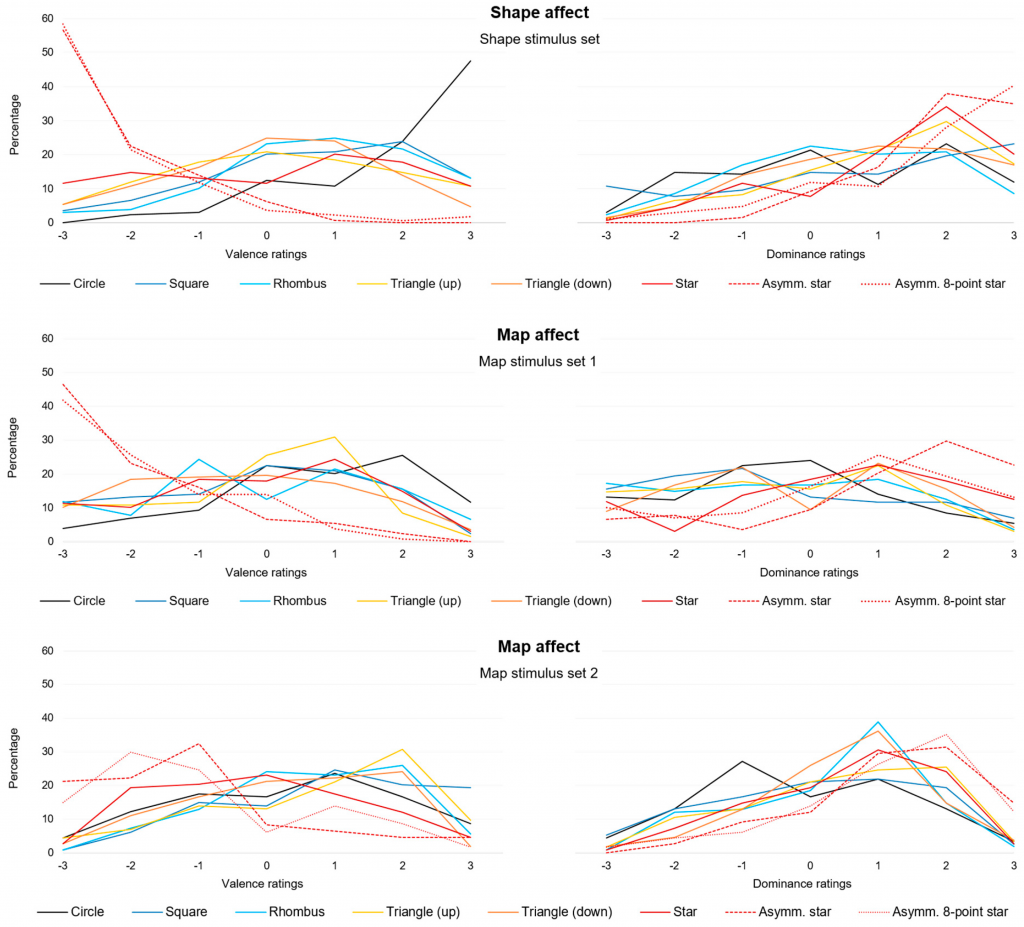
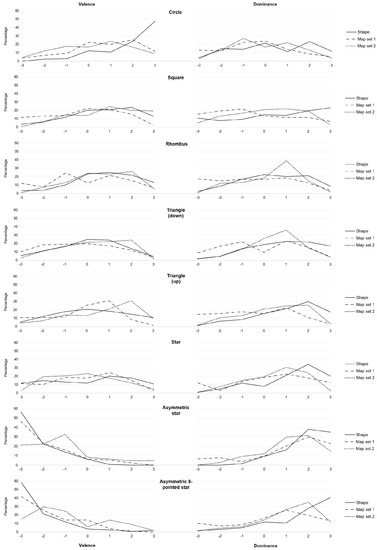
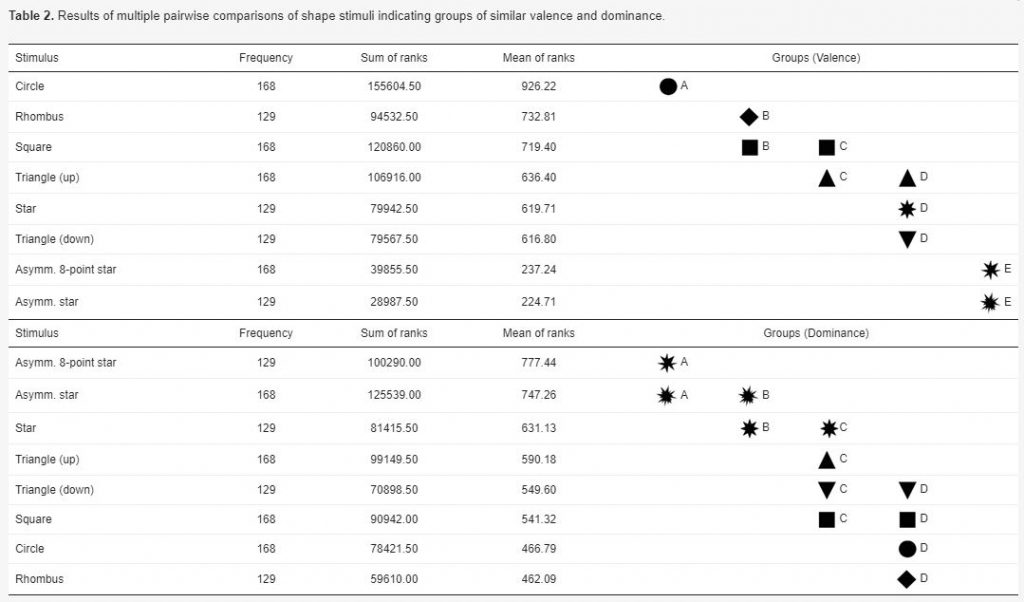
Maps enable us to relate to spatial phenomena and events from viewpoints far beyond direct experience. By employing signs and symbols, maps communicate about near as well as distant geospatial phenomena, events, objects, or ideas. Besides acting as identifiers, map signs and symbols may, however, not only denote but also connote. While most cartographic research has focused on the denoting character of visual variables, research from related disciplines stresses the importance of connotative qualities on affect, cognition, and behavior. Hence, this research focused on the connotative character of map symbols by empirically assessing the affective qualities of shape stimuli.
Preview results:
Master thesis defense on solar shadow map
We congratulate Georg Molzer for finishing his Master’s studies with his thesis on “Interactive Web-based 3D Solar Shadow Map“.
Nowadays, the majority of people live in cities, consisting of ever taller building structures, occluding more and more sunlight. Thus, humans are getting increasingly restricted from direct access to the Sun. This thesis claims that a tool, enabling humans to gain a better understanding of solar shadows in cities and around the world, would be beneficial. […] Such a tool should be able to consider relevant three-dimensional occluding structures such as buildings, terrain, and vegetation, as well as the actual Sun position, and visualize respective shadows for arbitrary points in time, providing predictability of solar shadows. […] Therefore, a methodology towards a capable prototype implementation is framed […].
For more details visit the project website shadowmap.org.
Well done and best wishes for your future career!
COVID19 – information for students
Dear students,
due to the recommendations of our government, we would like to inform you that:
- classroom teaching is suspended and distance learning will be available form 16 March 2020 via TUWEL (for further information visit colab.tuwien.ac.at/display/CORONA/CORONA+Information_EN)
- public rooms and libraries are closed until further notice
- your lecturers from TUWien Research Division Cartography are available for you by email
- ! update: distant learning measures are
in place until 16 April 2020extended until the end of the summer semester 2020
Please, take care and keep yourselves updated about latest developments at:
Congratulations to Haosheng Huang
Congratulations to our former staff member and PhD Student Haosheng Huang to be appointed as Professor for GIS and Cartography at University Ghent!
Cartography in FUTUREZONE.at
The Austrian portal FUTUREZONE.at, has just released an article about how Google Maps has revolutionized our lives during the last 15 years. Georg Gartner was interviewed among other colleagues in the domain.

…
Wie Google Maps unser Leben revolutionierte. Schon 15 Jahre gibt es Google Maps. Unsere Sicht auf die Welt hat sich dadurch für immer verändert. Nicht nur zum Positiven.
„Googles Einstieg war eine Revolution, die eine neue Ära der Kartografie eingeläutet hat”… „Ging es bis dahin um das Produzieren einzelner Artefakte – also statischer, physischer Karten, die für die Ewigkeit gedacht waren – wurde die Karte jetzt plötzlich zur interaktiven Schnittstelle, die auch Dienstleistungen abbildet und nach eigenen Bedürfnissen personalisiert werden kann.”
…
Read the full article at: Futurezone
Volltext als PDF (3,3 MB) (Quelle: Futurezone)
Season’s Greetings from the Research Division Cartography
Dear colleagues and friends, we would like to thank you for the collaborations in 2019. We look forward to working with you in the upcoming year!
Our best wishes for a pleasant holiday season and a prosperous New Year!

Open position in the cartography group
The Research Division Cartography is looking for a pre-doc University Assistant for 2.5 years, starting on 1 Feb 2020. All details [in German]:
Am Department für Geodäsie und Geoinformation , Forschungsbereich Kartographie E120-06 ist voraussichtlich ab 1. Februar 2020 für die Dauer von 2,5 Jahren eine Stelle für eine_n Assistenten_in, Gehaltsgruppe B1, mit einem Beschäftigungsausmaß von 30 Wochenstunden zu besetzen.
Das monatliche Mindestentgelt für diese Gehaltsgruppe beträgt derzeit EUR 2.148,40 (14x jährlich). Aufgrund tätigkeitsbezogener Vorerfahrungen kann sich das Entgelt erhöhen.
Aufnahmebedingungen:
abgeschlossenes Magister-, Diplom-, oder Masterstudium der Fachrichtung Kartographie, Geoinformatik, Informatik mit Schwerpunkt Visualization, Geodäsie bzw. gleichwertiges Universitätsstudium im In- oder Ausland
Sonstige Kenntnisse:
Die Bewerberinnen/Bewerber müssen zum Zeitpunkt des Stellenantritts ein einschlägiges Diplom- oder Masterstudium im Bereich der Kartographie, Geoinformatik, Informatik mit Schwerpunkt Visualization, Geodäsie oder Geographie abgeschlossen haben.
Der/Die Stelleninhaber/in soll im Bereich von Kartographischen Informationssystemen, insbesondere im Kontext von Location-based Services, arbeiten. Daher soll sie/er über sehr gute Kenntnisse in diesem Bereich sowie von Kartographischem Design, Methoden des WebMapping und von Visualization-Techniken verfügen. Außerdem sind sehr gute GIS und Programmierkenntnisse (bevorzugt JavaScript und Python) erwünscht. Für weitere Auskünfte zu dieser Ausschreibung stehen Ihnen Prof. Dr. Georg Gartner ( georg.gartner@tuwien.ac.at ) zur Verfügung.
Bewerbungsfrist: bis 16.01.2020
Bewerbungen richten Sie an die Personaladministration, Fachbereich wiss. Personal der Technischen Universität Wien, Karlsplatz 13, 1040 Wien, Onlinebewerbungen an barbara.triebl-kraus@tuwien.ac.at
Die Bewerber und Bewerberinnen haben keinen Anspruch auf Abgeltung angefallener Reise- und Aufenthaltskosten, die aus Anlass des Aufnahmeverfahrens entstanden sind.
LBS 2019 on-air
The Austrian national radio station Ö1 joined LBS2019 to capture the latest developments and ongoing research on Location Based Services: “Die Tücken der elektronischen Karten – Wie GPS die Welt(sicht) verändert” (starting at 19:18) is available in German until 29.11.2019, with interviews with Gartner Gartner, Georg Molzer, and Anita Graser.
For centuries, humans used maps to orientate themselves by land, by sea or to find their way. Nowadays, Location-Based Services are capable to provide such – and much more – information tailored to the users’ contexts. Last week, the international conference LBS2019 took place in Vienna to discuss ongoing research, projects, and challenges.